What's to know about radiation sickness?
Ionizing radiation happens when the atomic nucleus of an unstable atom decays and starts releasing ionizing particles.
When these particles come into contact with organic material, such as human tissue, they will damage them if levels are high enough, in a short period of time. This can lead to burns, problems with the blood, gastrointestinal system, cardiovascular and central nervous system, cancer, and sometimes death.
If an accident happens, for example, the earthquake in Fukushima, Japan, in 2011, or the explosion at Chernobyl, Ukraine in 1986, radiation can become dangerous.
Radiation Health Effects
Ionizing radiation has sufficient energy to affect the atoms in living cells and thereby damage their genetic material (DNA). Fortunately, the cells in our bodies are extremely efficient at repairing this damage. However, if the damage is not repaired correctly, a cell may die or eventually become cancerous. Related information in Spanish.
Exposure to very high levels of radiation, such as being close to an atomic blast, can cause acute health effects such as skin burns and acute radiation syndrome (“radiation sickness"). It can also result in long-term health effects such as cancer and cardiovascular disease. Exposure to low levels of radiation encountered in the environment does not cause immediate health effects, but is a minor contributor to our overall cancer risk.
Fast facts on radiation sickness:
- Nuclear accidents, the work environment, and some medical treatment can all be sources of radiation poisoning.
- Depending on the dose, the effects of radiation can be mild or life-threatening.
- There is no cure, but barriers can prevent exposure and some medications may remove some radiation from the body.
- All the American flags placed on the moon are now white due to radiation from the sun.
- 1% of static on an untuned analog TV is from cosmic background radiation from the Big Bang .
- A handful of raw uranium ore actually only has about as much radiation as 10 bananas.
- Astronauts on the Apollo missions reported seeing flashes and streaks of light when they closed their eyes. This was later confirmed to be caused by cosmic radiation bombarding their retinas while outside of the Earth’s magnetosphere.
radiation sickness
Radiation poisoning happens when a radioactive substance gives off particles that get into a person's body and cause harm. Different radioactive substances have different characteristics. They can harm and help people in different ways, and some are more dangerous than others.
How much radiation is dangerous ?
- Below 30 rads: Mild symptoms will occur in the blood
- From 30 to 200 rads: The person may become ill.
- From 200 to 1,000 rads: The person may become seriously ill.
- Over 1,000 rads: This will be fatal.
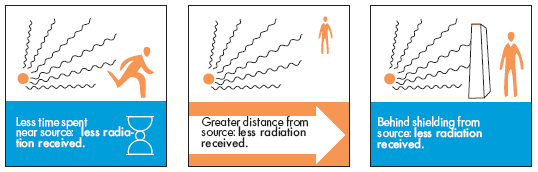
Protection
Possible treatments include:
- Removing all clothing,
- Rinsing with water and soap.
- Use of potassium iodide (KI) to block thyroid uptake if a person inhales or swallows too much radioiodine
- Prussian blue, given in capsules, can trap cesium and thallium in the intestines and prevent them from being absorbed. This allows them to move through the digestive system and leave he body in bowel movements.
- Unlikely a woman is pregnant in the first ten days following her period
Use for high dose procedures. - Radiation dose shall not exceed limits recommended for the appropriate circumstances.

0 Comments
Post a Comment